Breathing in contaminated air.
might send out soot far beyond a pregnant lady’s lungs, all the method to the womb.
surrounding her establishing child.
Samples of placenta.
gathered after ladies in Belgium delivered exposed soot, or black carbon, ingrained within the tissue on the side that deals with the child, scientists report.
online September 17 in Nature.
Communications The quantity of black carbon in the placenta associated with.
a female’s air contamination direct exposure, approximated based upon emissions of black carbon near.
her house.
” There’s no doubt.
that air contamination hurts an establishing child,” states Amy Kalkbrenner, an.
ecological epidemiologist at the University of Wisconsin– Milwaukee who was.
not associated with the brand-new work. Moms who.
encounter air contamination frequently might have infants born too soon or with low birth weight( SN: 5/13/15).
These developmental issues.
have actually been connected to an inflammatory reaction to air contamination in a mom’s body,.
consisting of swelling within the uterus. However the brand-new research study, Kalkbrenner states, recommends that “air.
contamination itself is entering into the establishing child.”
The research study looked.
especially at black carbon, a toxin produced in the burning of fossil.
fuels such as fuel, diesel and coal. Scientists in Belgium at Hasselt.
University in Diepenbeek and Katholieke.
Universiteit Leuven utilized femtosecond pulsed laser lighting to evaluate the tissue.
for soot. The method includes utilizing very quick laser bursts– each one-quadrillionth.
of a 2nd– to thrill electrons within the tissue, which then gives off light. Various.
tissues are understood to produce specific colors, such as red for collagen and.
green for placental cells. The black carbon stood out and launched white.
light.
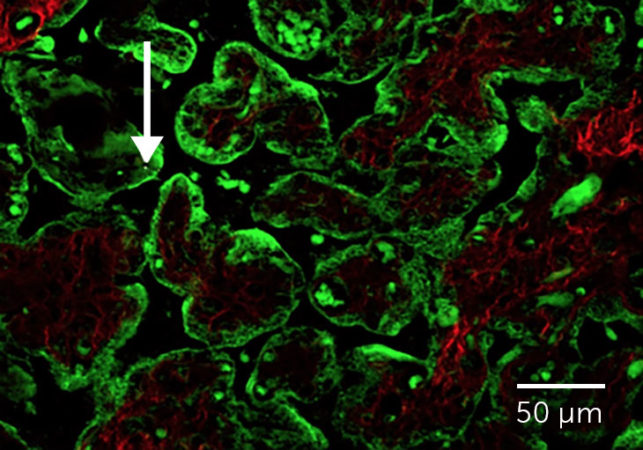
” The black carbon particles genuinely stand.
out distinctively” from the remainder of the tissue, states Bryan Spring, a biomedical.
physicist from Northeastern University in Boston who was not associated with the work.
The scientists likewise took a look at whether.
the quantity of black carbon found in placental samples matched a female’s air.
contamination direct exposure, approximated based upon where she resided in the northeast of.
Belgium. More soot was discovered in the samples from ladies who experienced greater contamination.
levels in their suburbs.
Kalkbrenner discovers it assuring “that.
they’re getting a real connection where greater procedures of the air.
contamination … accompanied greater procedures of black carbon particles.” The research study.
recommends it may be possible to evaluate for an individual’s direct exposure to contamination from.
tissue samples and even blood, she states. Presently, researchers mostly.
price quote contamination direct exposure based upon where an individual lives, which can exclude.
other sources such as those experienced at work.









